About product.
BAS ERP is a software package that allows you to organize a single information system to manage various aspects of the enterprise.
The program is designed to automate the activities of large enterprises with technically complex production and a large number of jobs. In today’s market conditions, there is no company that would not use automation tools in their work.
Programs that provide the ability to automate all business processes within a single information base are the basis for creating ERP-systems.
The BAS ERP application solution is a new product that is focused on large enterprises and is aimed at automating the tasks of enterprise, process and personnel management.
Subsystems BAS ERP.
The BAS ERP solution easily integrates with CBT SCM. In the complex, both systems completely close the accounting and management circuit, as well as provide all the necessary planning and forecasting tools.
BAS ERP software solution helps to manage aspects of enterprise management and includes the following subsystems:
Accounting and tax accounting;
Settlements with clients;
Warehouse and delivery;
Treasury;
Financial Accounting;
IFRS;
Budgeting;
Production management;
Repair management;
Procurement Management;
Personnel management and salary;
Sales management;
Control and management
Electronic equipment;
Exchange with websites;
Work in web;
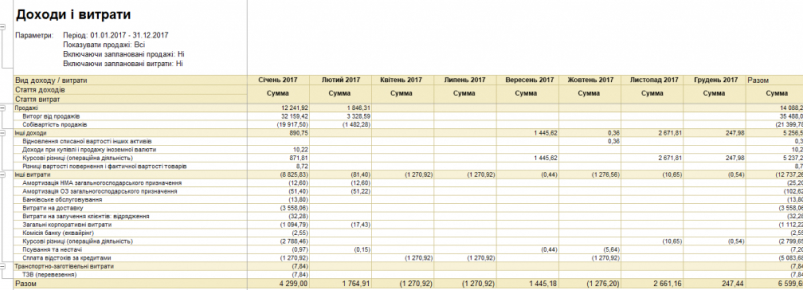
Accounting and tax accounting.
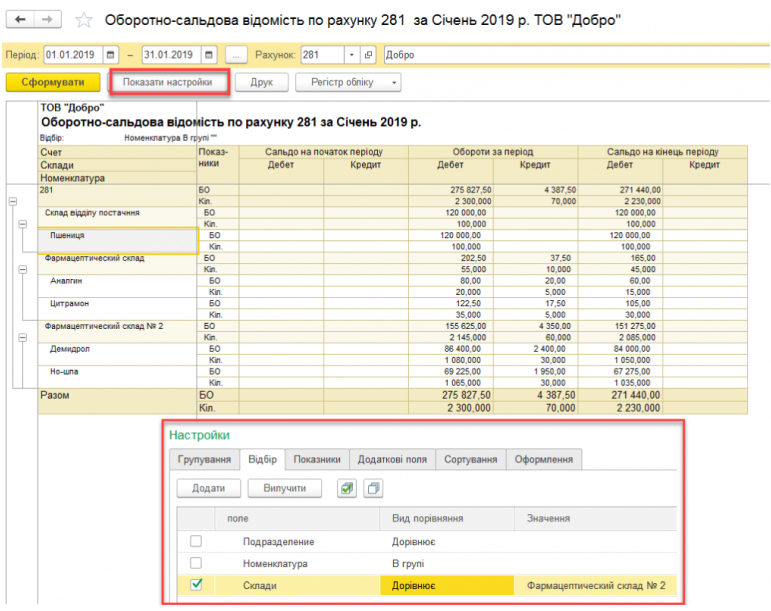
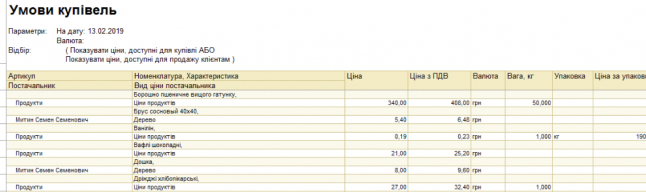
The configuration includes standard reports that allow you to analyze the balances, account turnover and postings in different sections. The functionality provides the ability to group, select and sort information that will be displayed in the report, based on the specifics of the enterprise. It is possible to download reports in e-mail. kind of.
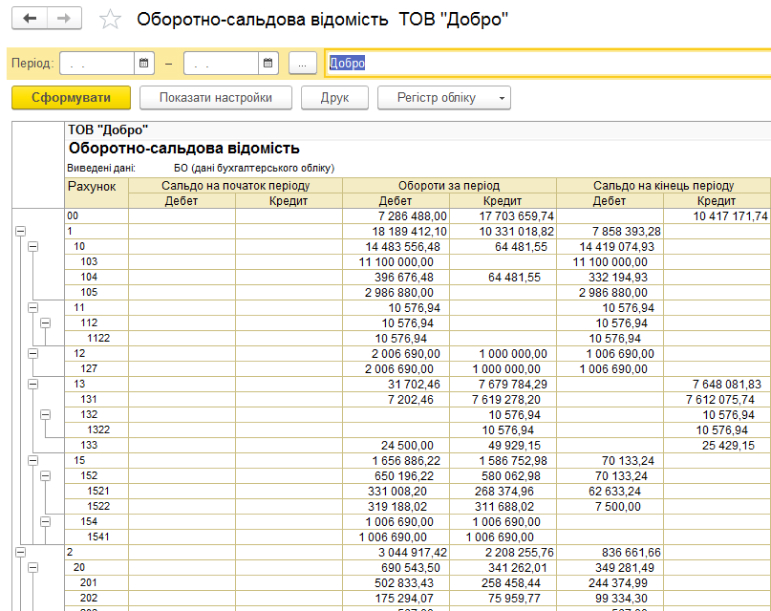
Mutual settlements with clients.
The subsystem provides optional functionality:
- Use of standard and individual rules of work with clients (offers). However, you can register transactions without offers;
- Using several options for planning payments from customers;
- Automation of pre-sales work with customers with the help of commercial offers;
- Use of the order scheme of document circulation of sales;
- Use of order reconciliation processes, order statuses and states;
- Planning and registration of returns of goods from customers;
- Conducting claims work with clients;
- Use of acts on the transfer of rights and acts of disagreement after the sale of products / services;
- The use of mechanisms for the implementation of nomenclature prices, including the use of information base data and supplier prices.
Potential economic effect from the use of the subsystem functionality:
- Increasing the volume of sales of goods and services;
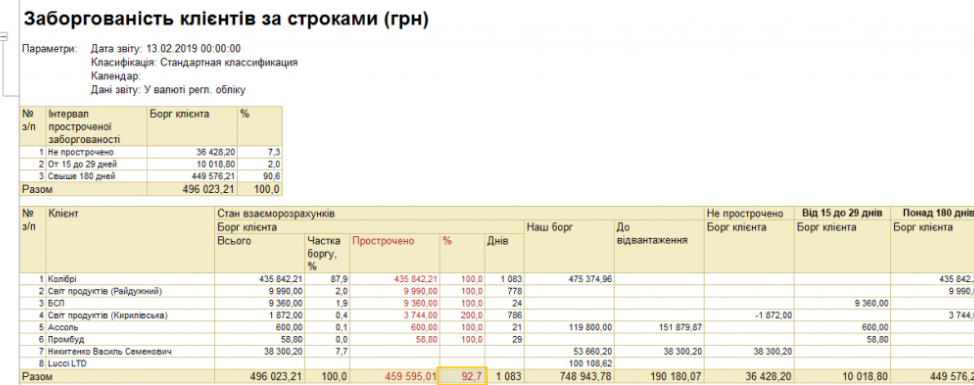
- Increase in turnover due to control of receivables;
- Reduction of orders execution terms
- Improving the accuracy of planning individual orders through separate accounting of orders;
- Optimizing pricing and increasing attractiveness for customers, in particular through the use of self-service interface;
- Reducing labor costs for the preparation of documents and increasing staff productivity;
- Improving the quality and transparency of staff through the ability to analyze the financial results in terms of departments and managers;
- Unification of staff work and reduction of labor costs due to the mechanism of business processes, standard offers and interactions;
- Improving the company’s rating in terms of potential investors and partners through the use of management practices that would meet international standards.
Warehouse and delivery.
The main task of this subsystem is the automation of warehousing operations of the enterprise, including technological processes of warehousing and delivery operations, namely:
- Planning and control of warehousing operations;
- Optimization of technological processes of the warehouse, where address storage is used, in particular during inventory;
- Planning and control of delivery processes.
Potential economic effect from the use of the subsystem functionality:
- Reduction of logistics costs by optimizing the operation of warehouses and delivery planning;
- Reduction of losses from damage to inventories;
- Reduction of labor costs for the preparation of documents and increase the productivity of staff;
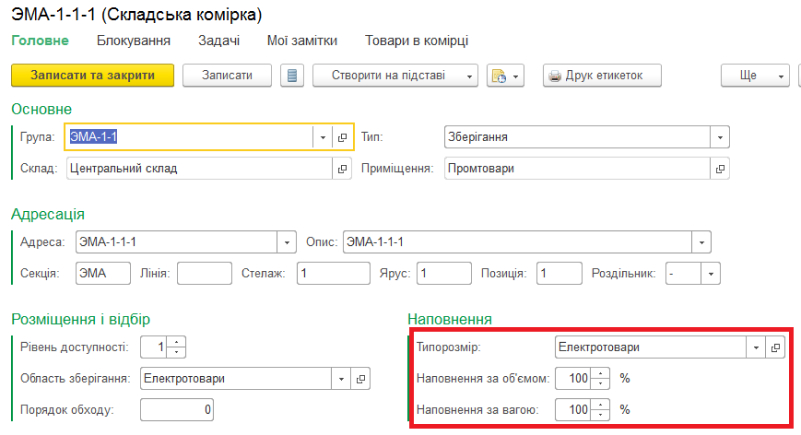
The functionality of the subsystem provides the ability to automate warehousing operations in the simplest case, without the use of the order scheme of document circulation, with the use of the order scheme of document circulation and with the use of address storage. The variant of the used document circulation is specified for each structure.
WMS warehouse management system.
The functionality of the system allows:
- to keep quantitative records of goods in warehouses and premises;
- keep records of goods at the level of warehouses for targeted storage of goods;
- divide storage areas into work areas;
- division of the warehouse into storage zones of different groups of goods (meat, eggs, clothing, appliances, etc.);
- optimal selection of cell size in accordance with the dimensions of the product.
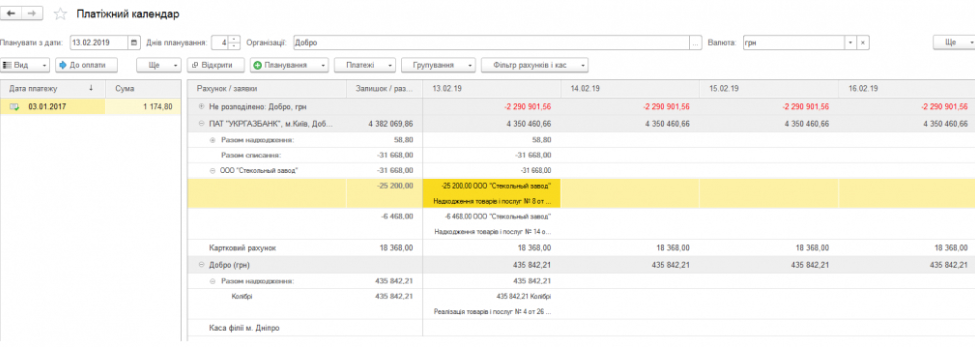
Treasury.
The task of the subsystem is the effective management of funds, which are the main source for the formation of production resources of the enterprise needed to implement strategic plans.
The subsystem allows you to automate the following functions:
- Cash flow planning;
- Accounting for cash and non-cash cash flows, including in different currencies;
- Monitoring the execution of the payment schedule and its change, if necessary;
- Make settlements with accountable persons.
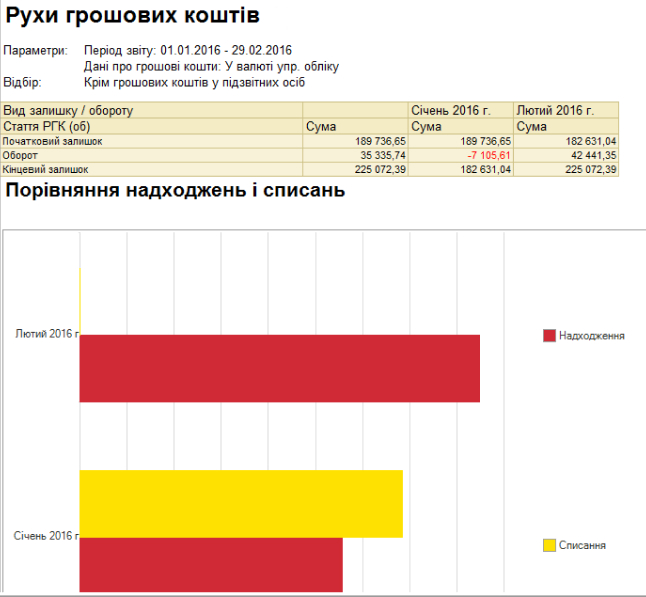
Potential economic effect from the use of the subsystem functionality:
- Reduce the time of checking payment registers through the use of a payment calendar;
- Improving the efficiency of the use of funds;
- Reduction of operating and management costs;
- Reduce labor costs for the preparation of documents and increase staff productivity.
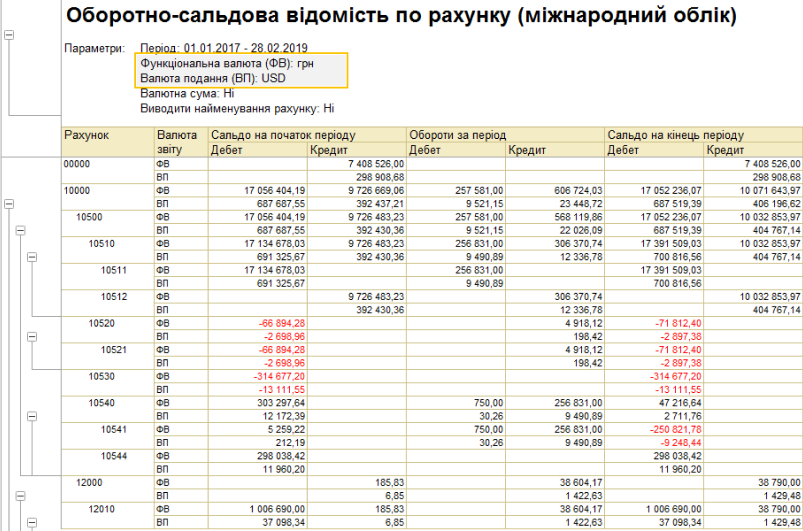
Financial Accounting.
The financial management subsystem allows:
- Register / distribute income and expenses by activities;
- Take into account other income and expenses – regulate the registration in the information base of income and expenses not related to the main activity;
- Take into account other assets and liabilities – regulate the registration in the information database of movements on assets and liabilities not related to the main activity;
IFRS.
International Financial Accounting (IFRS) helps to solve the following tasks:
- display of operational accounting documents in financial accounting;
- preparation of reports:
- in accordance with the principles of international financial reporting standards, including the ability to configure additional reports to verify and analyze accounting data;
- according to the rules of management accounting, built on the basis of IFRS;
- setting the frequency of reporting (month, quarter, half-year, year), as well as flexibility in setting up the following reporting forms:
- Statement of financial condition;
- Statement of comprehensive income;
- Statement of changes in equity;
- Statement of Cash Flows.
- reduction of labor costs for reporting compared to manual reporting by a staff specialist or outsourcing specialist
The use of IFRS is optional and is included separately as required by the entity.
In this subsystem, in the user mode, the currencies required for use are set, the conditions under which accounting will be set are set, namely from which sources the data in IFRS will be transmitted:
- Formation of postings according to operational accounting;
- Formation of postings according to the regulated accounting;
- Independent accounting of non-current assets for international accounting.
Budgeting.
The budgeting subsystem is designed for:
- Planning of financial indicators of economic activity, in particular planning of cash flows, sales, purchases, production, operating expenses;
- Formation of financial statements based on actual and planned data.
The purpose of the subsystem is the organization of data management processes, which provide an opportunity to get a clear picture of both current and future financial condition of the enterprise on selected indicators (profit, cash balances, etc.). Budget forms are a tool for organizing such processes.
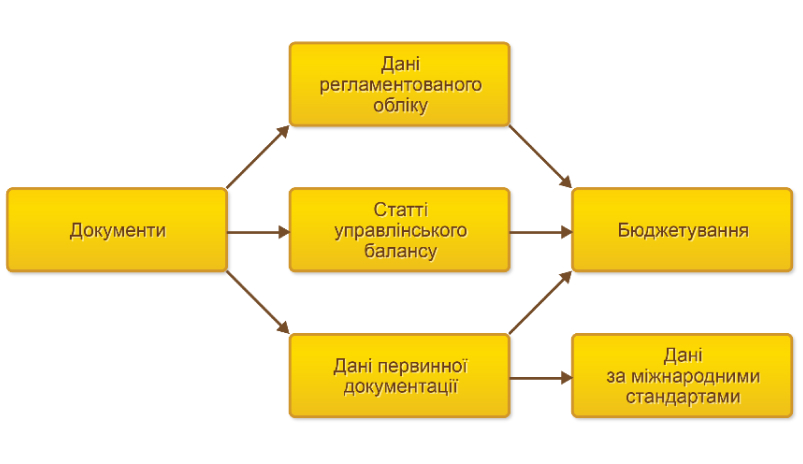
The budgeting subsystem provides the ability to:
- Plan the financial condition of the enterprise for the specified period;
- Plan cash flows;
- Prepare basic budgets and financial reports on the actual state of the enterprise:
- Revenue and expenditure budget;
- Cash flow budget
- Forecast balance;
- Prepare operational and functional budgets, and consolidated financial plan;
- Model future activities using different work scenarios, compare scenario data with each other;
- To form a plan-factual analysis of deviations in the context of selected analysts;
- Manage the processes of formation and approval of budgets, as well as analyze the results for the period;
The budgeting process is regulated only by the regulations on budgeting, which are developed and approved by the company.
The Budget Regulations approve:
- System of indicators;
- Structure of budgets (budget model);
- Budget regulations (planning, approval and control of implementation).
The main advantage of the subsystem is the lack of a specific model and the flexibility to configure the system.
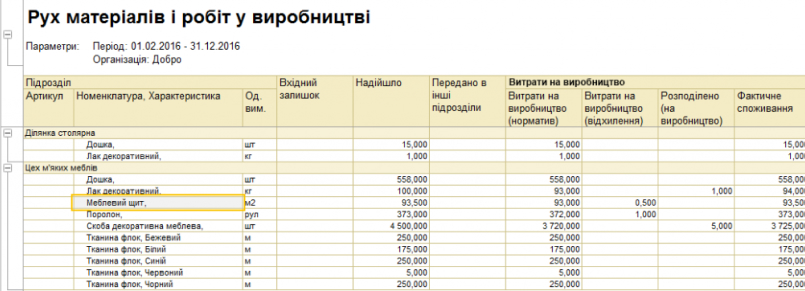
Production management.
The budgeting subsystem is designed for:
- At the inter-shop level (the level of the chief dispatcher) the control over the schedule of production at the level of divisions is carried out. This is a consolidated control over time and resources;
- At the in-shop level (local dispatcher level) the processes of production schedule execution in a separate subdivision are managed.
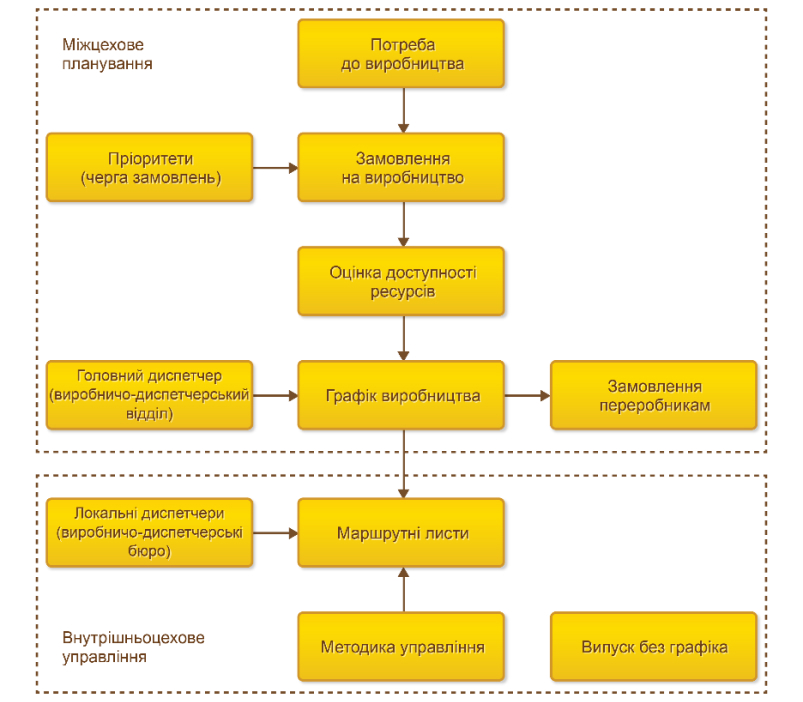
The functionality of the subsystem supports:
- Extensive control over the provision of all resources, ie not only at the level of availability of work centers, but also within the provision of material resources;
- Diagnosis and the ability to easily reschedule production schedules;
- Ability to forecast production orders, evaluate the fulfillment of orders, equipment loading, staff loading, etc.
Repair management.
The subsystem provides:
- Registration and storage of information on the objects of operation, the parameters of their operation, the parameters of their periodic maintenance and operation;
- Registration of information on defects and damages in the operation of facilities, the use of works to eliminate breakdowns;
- Recording of operations related to the life cycle of equipment (acceptance for accounting, modernization, etc.)
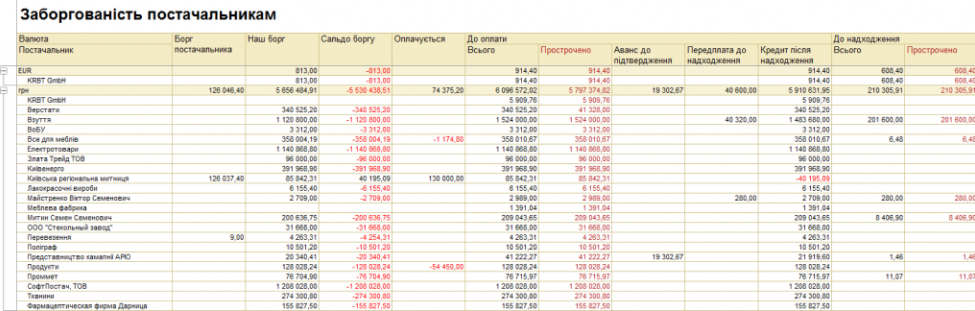
Procurement management.
The subsystem provides optional functionality:
- Use of the order scheme of document circulation of purchases;
- Use of order reconciliation processes, order statuses and states;
- The use of acts of acceptance of goods and acts of disagreement found in the registration of receipt of goods;
- Registration of differences in the receipt of goods and reflection of these differences in accounting;
- Use of several mechanisms of registration of prices of suppliers, in particular loading of price lists of suppliers from external files;
- Storage of nomenclature names used by suppliers (supplier nomenclature), and use of supplier nomenclature in electronic document management, in particular in the case of downloading orders and price lists;
Potential economic effect from the use of the subsystem functionality:
- Optimization of costs for purchasing activities of the enterprise;
- Reduction of order execution terms
- Improving the accuracy of planning individual orders through separate accounting of orders;
- Reducing the cost of inventories;
- Reducing labor costs for the preparation of documents and increasing staff productivity;
- Reduction of operating costs by minimizing penalties from suppliers;
- Reduction of damage from damage and loss of returnable packaging.
Personnel management and salary.
The subsystem is designed to keep personnel records and information about all employees.
The program has built-in functionality for selection, training and evaluation of staff skills, working time management.
Many types of accruals are provided for calculators – salaries, piecework salaries, payment of material assistance, income in kind.
Accrual and withholding of taxes in accordance with the current legislation of Ukraine. Regular reports are provided for submission to regulatory authorities.
Sales management.
The subsystem provides optional functionality:
- use of standard and individual rules of work with the client;
- use of several payment options from the client;
- automation of pre-sales work with customers, with the help of commercial offers;
- use of the order scheme of document circulation of sales;
- use of order reconciliation processes, order statuses and states;
- planning and registration of goods returns from
- use of acts on the transfer of rights and acts of disagreement after implementation;
- use of nomenclature price registration mechanisms, using information base data and supplier prices;
- commission and retail operations;
- questionnaires;
- creation of templates for e-mail mailings and messages;
- formation of discounts;
- bonus program settings;
- analysis and processing of claims;
- CRM system;
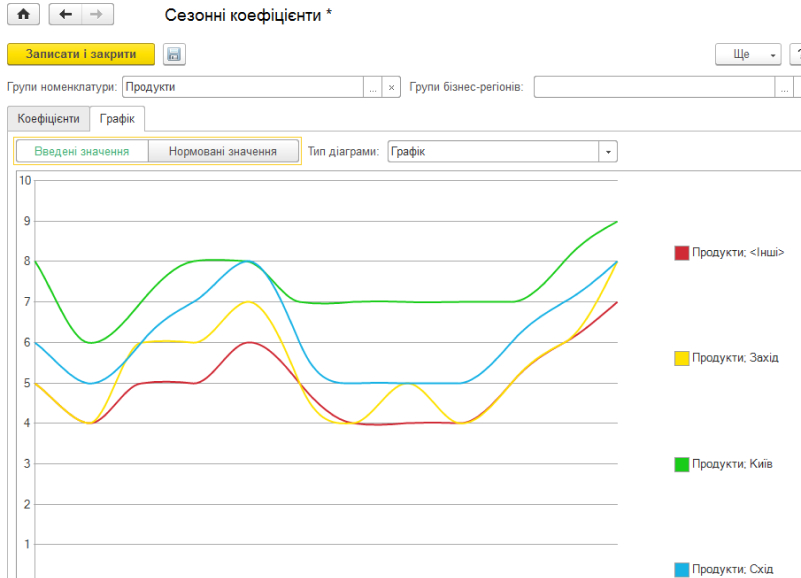
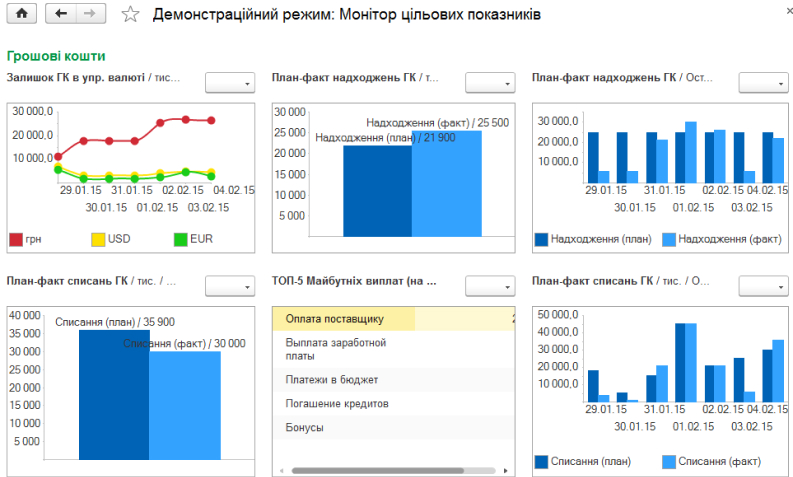
The analysis of target indicators is carried out in a special workplace – the Monitor of target indicators.
Within the framework of the subsystem functionality, the following concept of building balanced targets has been implemented:
- To maintain the strategic perspectives of management, the Handbook of Objectives category is used. The main task of the directory is to group the goals according to their purpose.
For example, financial goals, customer engagement goals, learning goals, development goals.
- The created list of goals or targets is stored in the directory Structure of goals ;
- For each target, the options for analysis and the target value we want to achieve are set. Analysis options are stored in the “Target Analysis Options” directory. Target values are stored in the Information Register. The target values of the analysis options can be set separately for each analysis option.
E-commerce equipment.
To date, there is a wide range of different equipment that is focused on use in trade. If you plan to use a software and hardware complex consisting of an information base and electronic trade equipment, then before starting work it is necessary to establish a connection between the equipment and the information base.
BAS ERP functionality supports interaction with the following types of trade equipment:
- Cash registers. Includes 2 modes of interaction with the program:
- Offline mode;
- fiscal registrar mode;
- Barcode scanners;
- Buyer’s displays;
- Electronic scales;
- Data collection terminals.
The software supply includes installed (integrated into the configuration) processing and drivers.
After selecting the “Save and Close” command, the configuration will automatically install the driver with built-in operating modes.
When interacting with merchant equipment, maintenance processing can be like using a merchant hardware driver to store information collected during remote data collection, such as when you need to use a warehouse inventory terminal without carrying a computer and then transferring it. collected DCT information in the work PC, and interact with the equipment directly by installing it, for example, directly at the checkout and immediately transfer the information from the DCT to your accounting system.
The use of maintenance treatments eliminates the need to make configuration changes due to the prescribed rules of interaction, which indicate to the program how to process information from the DCT in case of new updates, changes in the DCT itself, or when trying to connect devices that were not previously supported in the configuration.
Exchange with websites.
BAS ERP allows you to exchange data with online stores, perform the most important operations – unload the nomenclature and exchange customer orders.
The exchange of data with websites involves several stages:
- Setting up data exchange with sites;
- data exchange with websites.
To exchange data between the site and BAS ERP, the user must be assigned a role with full rights.
The following methods of data exchange are supported in the BAS ERP system:
- unloading of goods;
- exchange of orders;
- unloading of goods and exchange of orders.
It is possible to exchange data with the site in the following ways:
- directly with the site (Internet access required);
- by uploading / downloading data via files (does not require Internet access).
Work in the Web.
Modern technology is not standing still and BAS ERP developers continue to improve this software product. One of such modern solutions of BAS ERP is work with the help of a thin client and through a web-interface.
The user can work with the program through popular web browsers – Google Chrome, Opera, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, Edge, which gives the privilege of not being tied to the workplace.
The appearance of the program in the thin client and in the web-browser functions and looks almost identical.
The cost of implementing BAS ERP.
The first thing I want to note is that we do not recommend starting a project that automates from 5 jobs or more, without prior diagnostics of the field of automation, except for projects where it is really needed and the goal justifies the means. Only after it it is possible to make rather exact estimation of terms and cost of introduction, and the main thing is guaranteed to receive result.
Second. As you know, nothing can be automated “perfectly”, the automation process is like a repair, endless. Diagnosis allows you to record the functional framework of the project and the cost of them.
Third, the project charter is the one that allows to establish the logical framework of the project, to highlight the key roles of the project and those responsible. As you know, in a case for which everyone is responsible, in the end no one is responsible.
Fourth. It is necessary to implement a minimally viable product, beauty and convenience must be made in separate queues. This minimizes implementation risks.
Fifth. The business environment is changing rapidly, you should not “enter” the diagnosis, which lasts more than 3 months. According to our experience, a detailed technical task according to GOST has never described actual processes, because while it is being developed the company manages to change all or part of business processes. The main purpose of the diagnosis is to determine the scope of the project, cost and timing. The secondary goal is to identify business problems and offer solutions with the help of a software product.
But what to do at the stage when it is necessary to determine the cost of such implementation without or before diagnosis?
This may be necessary in order to assess the need to enter into the process of preliminary diagnostics for the implementation of BAS ERP, because it is known that such diagnostics often requires significant resources from the company of the implementer, and therefore can not be cheap. Another example is the situation when the implementation time is rapidly reduced, and the existing systems in the company clearly do not cope with the tasks and stop the business, so there is no time to perform quality diagnostics and there is a need to run without it on the most standard functionality. To do this, it is necessary at this stage to understand the fork of prices for implementation.
Let’s dwell on this in more detail.
How is the cost of the BAS ERP implementation project assessed, given the fact that the main resource of the project is certified specialists?
Given the fact that the main resource of the project are certified professionals?
Correctly, the amount of work carried out by such specialists is estimated, ie the time that must be spent on the implementation of a project, as we know time is measured in hours. From this we conclude that the cost of the implementation project depends on the number of hours spent by the specialist on the implementation of project tasks.
This is the formula for calculating the cost of the BAS ERP project of any implementer, including the Business Technology Center, both for Fixed price projects and for Time and materials projects.
Additionally, the cost of the software itself is taken into account. Calculation of such a project in the hours of specialists and is performed in the process of diagnosing the field of automation, the identified needs or tasks of automation. A project plan is drawn up, which includes standard implementation tasks and specifics of a specific business, the coverage of business tasks by the functionality of the implemented software or improvements of such software is formed.
Based on the experience of conducting such diagnostics, the company “Center of Business-Technologies” provides certain criteria by which you can determine the fork of prices without conducting diagnostics.
Cost of Software.
The first parameter. The cost of BAS ERP at the time of writing was UAH 180,000.00. without VAT (software is exempt from VAT in accordance with the Tax Code of Ukraine). It is also strongly recommended to purchase a server license (64 bit) for 5 or more users at a time, but not necessarily, which allows you to work with most common database management systems, such as Postgre and others.
The cost of such a license is UAH 42,600.00, or UAH 9,000. For a mini-server with 5 connections. Additionally, you will need to purchase competitive competition licenses, each of which will cost at least UAH 3,300, or UAH 11,610.00. For a set of 5 users.
* information is relevant at the time of writing (12-02-2019), is not a primary source and is for informational purposes only.

Training of employees.
The second parameter is the number of automated jobs. The number of hours for training of the customer’s employees depends on it. Thus, the training of one employee should be based on 16 to 24 hours for each such employee for the minimum possible implementation.
In reality, everything is much more complicated, because training can be performed in groups of general functionality, and individually with each of the specific capabilities. Key employees of the Customer can be involved in the training process.
But for a rough estimate, you should expect a minimum of ** 16-24 hours per user.
So the training of 5 users on average can cost from *** 2,600.00 to *** 4,200.00 USD depending on the department and the level of staff, the cost of the implementer, the number of certificates of the implementer, his experience and current workload.
** The assessment is based on the calculation of basic functionality with minimal viable training by a specialist and subsequent self-training of employees. The number of hours may be greater in each case and is determined in the diagnostic process.
*** Prices are presented to understand the fork of the minimum possible prices and are for informational purposes only, may not match the real prices in the market of BAS ERP implementers.
The third parameter is the work of transferring directories and initial balances from the old system. Thus, a minimum of 24 hours to 80 hours of work of developers / consultants may be required to start a standard wholesale business with 5 automated workstations for transferring balances, depending on the involvement of the implementer’s specialists (from training to automatic download) and data retrieval and processing difficulties. from the old system. Extra large reference books should be considered individually in the diagnostic process. This will additionally cost the customer at least from *** 800.00 USD to *** 2 800.00 USD.
*** Prices are presented to understand the fork of the minimum possible prices and are for informational purposes only, may not match the real prices in the market of BAS ERP implementers.
Also, the key but not the only factors influencing the cost of implementation include:
- The need and scope of improvements to identify or evaluate which is possible only after their study. There are improvements, but do not know how much they will cost? The Center for Business Technologies will help to pre-evaluate and help with the task.
- The level of the current state of processes in the enterprise. The scale and number of changes that need to be made to switch to BAS ERP depends on the level of processes;
- Staff interest in the implementation process, because at the implementation stage there is an increase in the work performed by the employee;
But the main thing you want to draw your attention to should be to trust companies that have experience in implementing programs of this level, which value their reputation.